| CPC B60W 50/0205 (2013.01) [B60W 60/001 (2020.02); G01S 19/20 (2013.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
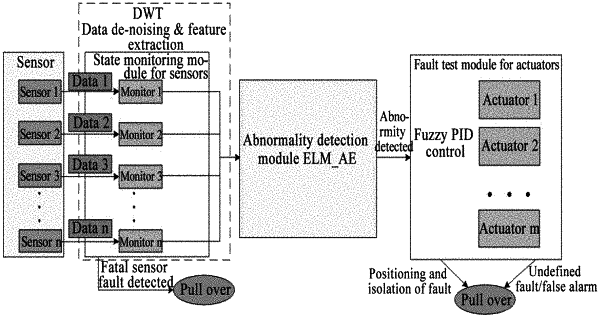
1. A method for a fault diagnosis of an intelligent vehicle, comprising:
1) establishing a model of a system of the intelligent vehicle; acquiring system operation data of the intelligent vehicle in a normal running state; training and optimizing the model using the system operation data of the intelligent vehicle in the normal running state; wherein, before training and optimizing the model, the sensor data of the system operation data of the intelligent vehicle in the normal running state is de-noised, and feature extraction and screening are performed for a fatal sensor fault of the system operation data of the intelligent vehicle in the normal running state;
2) collecting system operation data of the intelligent vehicle in a running state in real time; de-noising sensor data of the system operation data of the intelligent vehicle in the running state, and performing feature extraction and screening for a fatal sensor fault to reconstruct the system operation data of the intelligent vehicle in the running state; inputting the reconstructed system operation data into the trained model to output system state data of the intelligent vehicle in the running state; comparing the system state data with a set threshold; and if the system state data exceeds the set threshold, determining that an actuator corresponding to the system state data has a fault, thereby completing the fault diagnosis of the intelligent vehicle;
wherein in step 1) and in step 2), the fatal sensor fault is determined according to formulas (6) and (7):
thBM<abs(Σi=k-(W-1)kdi) (6),
thJ>Σi=k-WJk abs(x(k)−x(i)) (7),
wherein, thBM and thJ are two set thresholds and are set to be 3 and 1×10−6 respectively; W and Wj are sizes of two sliding windows and are set to be 100 and 50 respectively; di represents a three-level detail coefficient obtained through DWT at moment i; and x(k) represents the sensor data at moment k.
|