| CPC A61L 27/52 (2013.01) [A61L 27/225 (2013.01); A61L 27/3633 (2013.01); A61L 27/3808 (2013.01); A61L 27/3826 (2013.01); A61L 27/3886 (2013.01); A61L 27/58 (2013.01); B82Y 5/00 (2013.01); A61L 2400/12 (2013.01); Y10T 428/29 (2015.01); Y10T 428/2913 (2015.01); Y10T 428/2922 (2015.01); Y10T 428/2938 (2015.01)] | 34 Claims |
|
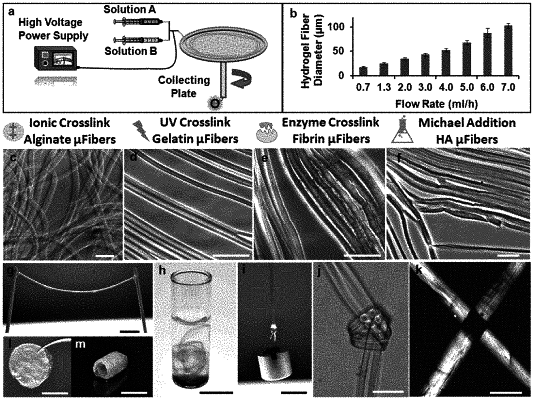
1. A biodegradable microfiber having a longitudinally aligned nanotopography comprising biodegradable, electro-mechanically stretched, hydrogel, polymers, wherein alignment of the polymers is stabilized during gelation of the hydrogel.
|