| CPC G06T 7/62 (2017.01) [A61B 5/02007 (2013.01); A61B 5/7264 (2013.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); A61B 6/032 (2013.01); A61B 6/504 (2013.01); G06T 7/0014 (2013.01); G16H 30/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); G06T 2207/10081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20021 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30101 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30172 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
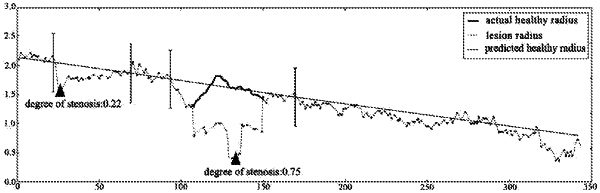
1. A computer-implemented method for predicting a blood vessel stenosis, the method comprising:
extracting a blood vessel path and its centerline based on an image of a blood vessel;
determining a candidate stenosis for the blood vessel path;
identifying image blocks along the centerline of the blood vessel path within a range of candidate stenosis for the blood vessel path determined based on the candidate stenosis; and
determining a degree of stenosis for the blood vessel path by applying a trained learning network comprising a convolutional neural network and a recurrent neural network on the image blocks within the range of candidate stenosis,
wherein the convolutional neural network and the recurrent neural network are sequentially applied, wherein the convolutional neural network is applied on the image blocks along the centerline of the blood vessel path to generate vectors for the respective image blocks, wherein the recurrent neural network is applied on the vectors.
|