| CPC G01S 7/4865 (2013.01) [G01S 7/484 (2013.01); G01S 7/4817 (2013.01); G01S 7/4861 (2013.01); G01S 17/10 (2013.01)] | 27 Claims |
|
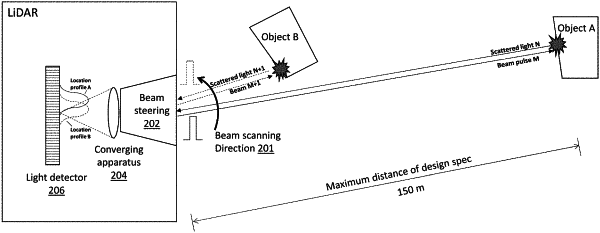
1. A light detection and ranging (LiDAR) scanning system configured for detecting a physical object by transmitting a light pulse and collecting a plurality of scattered light pulses, the system comprising an electrical processing and computing device configured to:
determine a plurality of candidate travel times associated with the plurality of scattered light pulses with respect to the transmitted light pulse;
obtain a plurality of location profiles corresponding to the plurality of scattered light pulses detected by a light detector;
determine, for each of the plurality of scattered light pulses with respect to the transmitted light pulse, a travel time based on the plurality of location profiles;
select a candidate travel time based on a correlation between the plurality of candidate travel times and the travel time determined for each of the plurality of scattered light pulses; and
calculate, based on the candidate travel time selected, a distance of the physical object from the LiDAR scanning system.
|