| CPC G01N 15/1434 (2013.01) [G01N 15/06 (2013.01); G01P 5/001 (2013.01); G01P 5/20 (2013.01); G01P 5/26 (2013.01); G01S 7/4916 (2013.01); G01N 2015/0693 (2013.01); G01N 2015/1454 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A particulate matter sensor, comprising:
a self-mixing interferometry sensor configured to generate a self-mixing interference signal;
a set of one or more optical elements positioned to receive an optical emission of the self-mixing interferometry sensor, split the optical emission into multiple beams, direct each beam of the multiple beams in a different direction towards a respective measurement region, and redirect received reflections or backscatters of the multiple beams from the respective measurement regions back into the self-mixing interferometry sensor to generate the self-mixing interference signal, wherein each of the multiple beams is separated from other beams of the multiple beams by 120 degrees in a plane perpendicular to an axis of the optical emission and each of the multiple beams has a secondary axis that diverges from the axis of the optical emission by a same angle θ; and
circuitry configured to:
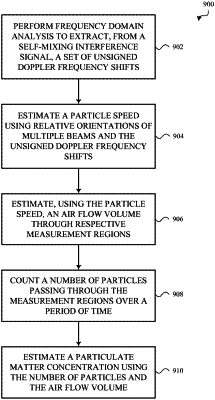
extract, from the self-mixing interference signal, particle speed information for particles passing through any of the multiple beams;
estimate a particle speed using the angle θ and using the particle speed information for particles passing through any of the multiple beams interchangeably;
estimate, using the particle speed, an air flow volume through respective measurement regions of the multiple beams;
count a number of time-domain disturbances in the self-mixing interference signal over a period of time, the number of time-domain disturbances corresponding to the number of particles passing through the respective measurement regions over the period of time; and
estimate a particulate matter concentration using the number of particles, and the air flow volume.
|