| CPC A61B 17/30 (2013.01) [A61B 1/00094 (2013.01); A61B 1/015 (2013.01); A61B 1/018 (2013.01); A61B 17/3478 (2013.01); A61M 5/315 (2013.01); A61B 2017/0034 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00269 (2013.01); A61B 2017/306 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
1. An endoscopic tool for facilitating injection of a fluid into a submucosal layer of tissue, the tool comprising:
a first cannula adapted to be slidably disposed within a lumen of an endoscope, the first cannula having a distal end, a proximal end opposite the distal end, and a lumen formed within the first cannula between the distal end and the proximal end of the first cannula;
means for attaching the first cannula to a mucosal layer of tissue;
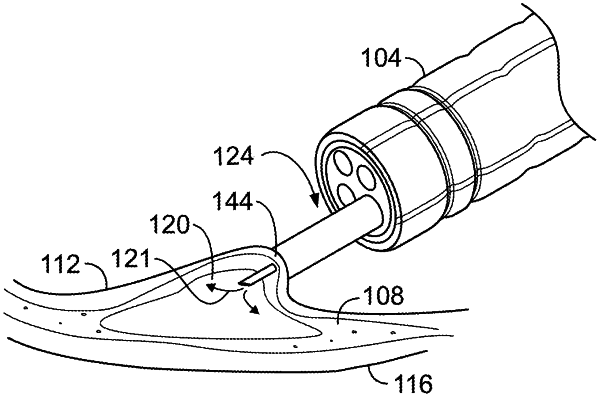
a second cannula adapted to be coupled to a source of a fluid to be delivered to a submucosal layer of tissue below the mucosal layer of tissue, the second cannula carrying a needle at a distal end of the second cannula; and
a needle stabilization structure coupled to the first cannula or the second cannula, the needle stabilization structure defining a fluid lumen separate from the lumen of the first cannula, the second cannula slidably disposed within the fluid lumen,
wherein responsive to attachment of the first cannula to the mucosal layer of tissue, the second cannula is movable toward the submucosal layer of tissue, causing the needle to pierce the mucosal layer of tissue and deliver the fluid into the submucosal layer of tissue.
|