| CPC G01V 1/50 (2013.01) [E21B 47/14 (2013.01); G02B 6/4401 (2013.01); G06F 17/18 (2013.01); G06N 3/084 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G01V 2210/646 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
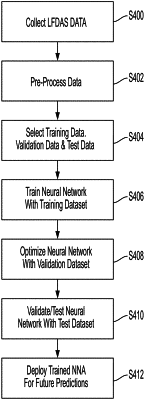
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
receiving a set of features for a first well proximate to a second well, the second well undergoing a hydraulic fracturing process for extraction of natural resources from underground formations, and the set of features including:
a summation strain rate, at a location associated with the set of features, during a set period; and
filtered data corresponding to the summation strain rate;
inputting the set of features into a trained neural network; and
providing, as output of the trained neural network, a probability of a fracture hit at the location associated with the set of features in the first well during a given completion stage of the hydraulic fracturing process in the second well.
|