| CPC G01N 1/44 (2013.01) [G01N 1/2035 (2013.01); G01N 27/12 (2013.01); G01N 33/0016 (2013.01); G01N 33/2823 (2013.01); G01N 2001/205 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. A method for measurement of the composition of a fluid, comprising:
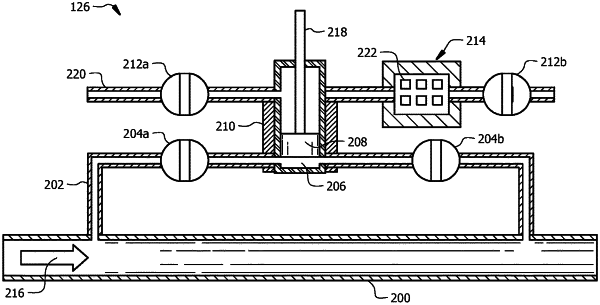
diverting a sample of a portion of the fluid from a main conduit into a diverting conduit through a first set of valves with a test chamber disposed between the first set of valves, wherein the test chamber comprises a piston disposed vertically above a central axis of the diverting conduit, a heat source disposed around the test chamber, and one or more electro-chemical resistor sensors, wherein the piston is in a first position;
actuating the first set of valves to close after the test chamber receives the sample of the portion of the fluid while the piston is in the first position;
moving the piston to a second position;
actuating the heat source to increase the temperature within the test chamber to produce vapors from the sample of the portion of the fluid after the piston is in the second position;
directing the vapors from the sample of the portion of the fluid to the one or more electro-chemical resistor sensor; and
determining a composition of the vapors from the sample of portion of the fluid, wherein the composition of the vapors is associated with the composition of the fluid.
|