| CPC E21B 49/081 (2013.01) [E21B 43/121 (2013.01); E21B 49/087 (2013.01); E21B 49/0875 (2020.05); G01N 21/359 (2013.01); G01N 21/3577 (2013.01); G01N 33/2841 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method for estimating clean fluid composition and properties, comprising:
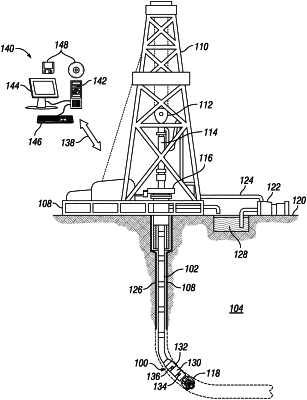
disposing a downhole fluid sampling tool into a wellbore, wherein the downhole fluid sampling tool comprises a fluid analysis module;
obtaining a fluid sample that has a contamination level for which a fluid property is not representative of a pure formation fluid with the downhole fluid sampling tool;
identifying input parameters from at least one sensor response on the fluid analysis module, wherein the input parameters comprise fluid properties indicative of the fluid sample and mud filtrate composition;
applying a robust regression method on at least one sensor response, wherein the robust regression method is computed as scoresfit=A+BXvβ, where A and B are constants determined by a regression method, v is a formation fluid pumpout accumulated volume, and β is a density decay rate; and
predicting a clean fluid sample of the fluid sample using a dimensional reduction analysis and an equation of state, wherein the equation of state utilizes one or more component mole fractions of the fluid sample.
|