| CPC G06Q 10/087 (2013.01) [G06N 5/04 (2013.01); H04L 9/0637 (2013.01); H04L 9/50 (2022.05)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A processing node comprising:
a memory storing one or more instructions; and
a processor that when executing the one or more instructions is configured to:
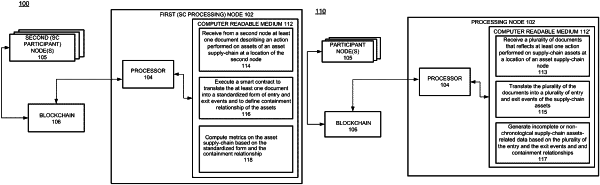
ingest, via a background process, a data stream comprising a plurality of documents from a plurality of supply chain nodes at a plurality of different locations which describe actions performed on containers by the plurality of supply chain nodes at the plurality of different locations,
execute machine-readable instructions within a blockchain smart contract on the plurality of documents;
transform, via the execution of the blockchain smart contract, a first set of documents from among the plurality of documents into locations of entry events with respect to the supply chain based on types of the first set of documents and rules within the blockchain smart contract;
transform, via the execution of the blockchain smart contract, a second set of documents from among the plurality of documents into locations of exit events with respect to the supply chain based on types of the second set of documents and the rules within the blockchain smart contract;
generate an incomplete model of the supply chain based on the locations of entry events and the locations of exit events,
infer missing events within the supply chain based on the locations of entry events and the locations of exit events and add the missing events to the incomplete model to generate an adjusted model of the supply chain;
receive a query associated with an asset being carried in a container, and
in response to the query, execute the query on supply chain data based on the adjusted model of the supply chain, and returning results of the query to a user device.
|