| CPC G06F 11/0736 (2013.01) [G06F 11/0724 (2013.01); G06F 11/0772 (2013.01); G06F 11/0793 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
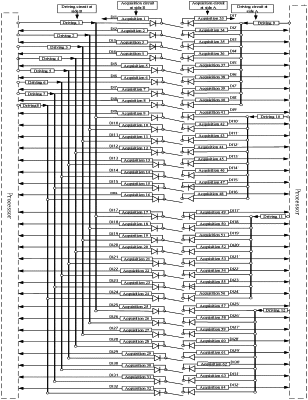
1. A two-sided time-sharing driving and acquisition system based on dry contacts, comprising k dry contacts, a processor, p acquisition circuits, and m driving circuits, wherein the k dry contacts are mutually independent, k, p and m are all positive integers, m≤p, and p=2k; the p acquisition circuits are evenly divided into two groups which are separately disposed at two sides of the k dry contacts, and the m driving circuits are separately disposed at the two sides of the k dry contacts;
an output of one of the m driving circuits is accessed to each of the two sides of each of the k dry contacts, driving signals at the two sides of each of the k dry contacts are from two of the m driving circuits separately, and the driving circuits at the two sides of each of the k dry contacts do not drive output signals at a same time; one of the acquisition circuits is connected to each of the two sides of each of the k dry contacts, and two corresponding acquisition circuits connected to each of the k dry contacts are independent of each other and are used for acquiring output signals of corresponding driving circuits at the two sides of the dry contact respectively;
the processor controls outputs of the m driving circuits at different times and reads signals acquired by the p acquisition circuits synchronously; if a given output signal of a given driving circuit at either side of one of the k dry contacts is acquired by the two corresponding acquisition circuits, the system determines that the one of the k dry contacts is in a close state; if the given output signal of a given driving circuit at either side of one of the k dry contacts is acquired only by the acquisition circuit at a same side, the system determines that the dry contact is in an open state; and in other cases, the system determines that a fault occurs.
|