| CPC G01S 17/86 (2020.01) [G01S 17/42 (2013.01); G01S 17/58 (2013.01); G01S 17/931 (2020.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
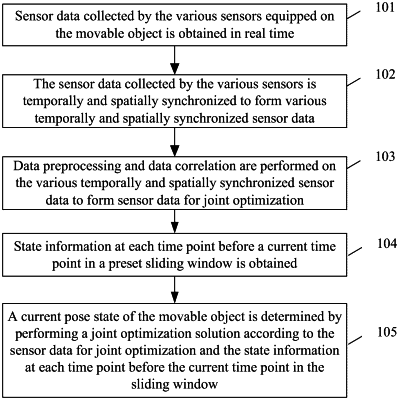
1. A positioning method based on multi-sensor fusion, applied to a movable object equipped with various sensors, the method comprising:
obtaining sensor data collected by the various sensors equipped on the movable object in real time, comprising:
obtaining IMU data measured by an IMU, wheel speed data of the movable object measured by a wheel speedometer, and point cloud data measured by a LiDAR in real time, wherein the various sensors comprise the IMU, the wheel speedometer, and the LiDAR, wherein the IMU comprises an accelerometer and a gyroscope;
temporally and spatially synchronizing the sensor data collected by the various sensors to form various temporally and spatially synchronized sensor data;
performing data preprocessing and data correlation on the various temporally and spatially synchronized sensor data to form to-be-jointly-optimized sensor data;
obtaining state information at each time point before a current time point in a preset sliding window comprising:
initializing state variables to form initialized state variables, wherein the state information comprises the state variables, and each of the state variables comprises a translation vector, a velocity vector, a rotation matrix, an IMU accelerometer bias, and an IMU gyroscope bias; and
determining a current pose state of the movable object by performing a joint optimization solution according to the to-be-jointly-optimized sensor data and the state information at each time point before the current time point in the preset sliding window, comprising:
determining the state variable at each time point in the preset sliding window by adopting a joint probability density estimation according to the initialized state variable at each time point before the current time point and the to-be-jointly-optimized sensor data, in response to no joint optimization being performed at each time point before the current time point in the preset sliding window, wherein the state variable at the current time point in the preset sliding window is used for representing the current pose state of the movable object; and
determining the state variable at each time point in the preset sliding window by adopting the joint probability density estimation according to the jointly optimized current state variable at each time point before the current time point and the to-be-jointly- optimized sensor data, in response to the joint optimization being performed at each time point before the current time point in the preset sliding window, wherein the state variable at the current time point in the preset sliding window is used for representing the current pose state of the movable object.
|