| CPC G01S 13/9027 (2019.05) [G01S 13/505 (2013.01); G01S 13/9011 (2013.01); G06V 10/62 (2022.01); G06V 10/761 (2022.01); G06V 10/762 (2022.01); G06V 10/809 (2022.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
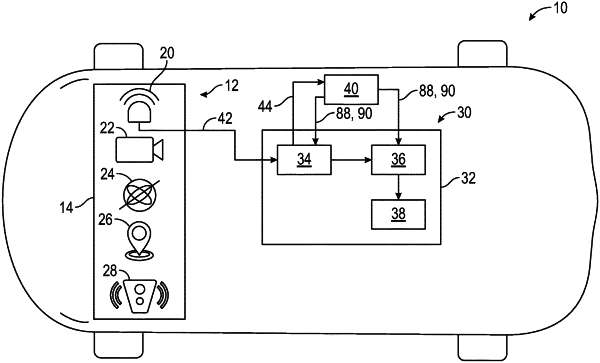
1. A radar anti-spoofing system for an autonomous vehicle, the radar anti-spoofing system comprising:
a plurality of radar sensors that generate a plurality of input detection points representing radio frequency (RF) signals reflected from actual targets; and
one or more controllers in electronic communication with the plurality of radar sensors, wherein the one or more controllers execute instructions to:
determine time-matched clusters that represent objects located in an environment surrounding the autonomous vehicle based on the plurality of input detection points from the plurality of radar sensors;
determine an adjusted signal to noise (SNR) measure for a specific time-matched cluster by dividing an SNR of the specific time-matched cluster by a range measurement of the specific time-matched cluster;
determine a motion-based velocity of the time-matched cluster based on a motion vector of the time-matched cluster;
determine a Doppler-frequency velocity of the time-matched cluster;
determine a velocity-ratio measure of the time-matched cluster by dividing the motion-based velocity by the Doppler-frequency velocity; and
identify the time-matched cluster as either a ghost object or a real object by a thresholding technique based on the values of the adjusted SNR measure and the velocity-ratio measure, wherein the thresholding technique includes selecting a threshold range of values for the adjusted SNR measure that capture a mismatch between an SNR and the range measurement that is created by the ghost object, and wherein the ghost object is produced by reciprocity-based spoofing where the RF signals are reflected from the actual targets but were originally emitted by a spoofer.
|