| CPC H02P 9/107 (2013.01) [H02P 23/08 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
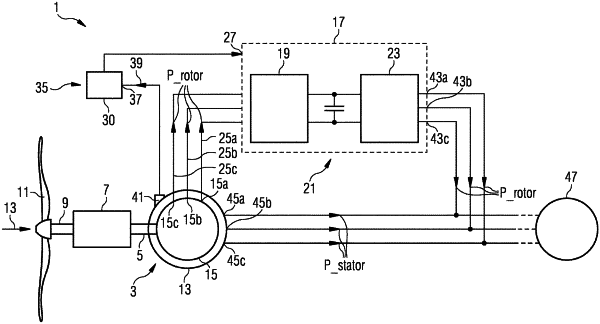
1. A method of controlling an induction generator connected to a utility grid, the method comprising:
receiving an actual grid frequency; and
controlling rotor windings of the generator by a rotor control signal having a rotor winding reference frequency (Ω_ref) being set in dependence of the actual grid frequency;
wherein the rotor winding reference frequency (Ω_ref) is set such that a slip (s) adheres to a predefined value and substantially does not change with changing actual grid frequency (f) at least in a predefined frequency range of the actual grid frequency,
wherein the slip (s) is given by:
s=(Ω(f)−ns(f))/ns(f),
wherein:
f is the actual grid frequency,
Ω is the actual speed of generator at the actual grid frequency f,
ns(f) is a synchronous speed at the actual grid frequency f,
wherein ns in rpm is given by ns=60*f/p, wherein p is the number of pole pairs of the generator rotor and f is given in Hz.
|