| CPC H02J 50/80 (2016.02) [H01F 27/24 (2013.01); H01F 27/28 (2013.01); H01F 27/36 (2013.01); H01F 38/14 (2013.01); H02J 50/12 (2016.02); H02J 50/50 (2016.02); H02J 50/70 (2016.02)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A power transmitter comprising:
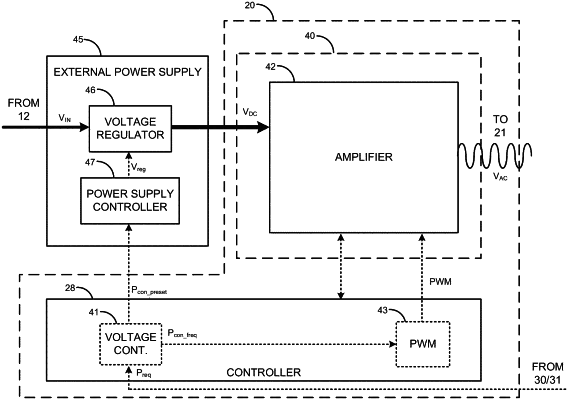
a transmitter controller configured provide a driving signal and a power control signal, the driving signal configured to generate an alternating current (AC) power signal for transmitting wireless power and the power control signal configured to control input from an external power supply, the transmitter controller comprising:
at least one first processor,
at least one first non-transitory machine-readable medium, and
first program instructions provisioned on the at least one first non-transitory machine-readable medium;
a power input in operative association with the external power supply and configured to receive a direct current (DC) input power from the external power supply;
an inverter circuit configured to (i) receive the DC input power via the power input, (ii) receive the driving signal, and (iii) convert the DC input power to the AC power signal, based on the driving signal; and
a transmitter coil configured to, based on the AC power signal and upon receipt of the AC power signal, transmit a wireless power transmission to a receiver coil of a power receiver,
wherein the first program instructions provisioned on the at least one first non-transitory machine-readable medium, when executed by the at least one first processor, cause the transmitter controller to:
determine a power requirement for the wireless power transmission,
determine the power control signal based on the power requirement, the power control signal configured to instruct the external power supply to select a DC voltage for the DC input power from a set of DC voltage levels, the set of DC voltage levels comprising a first DC voltage level associated with a first AC power signal level and a second DC voltage level that is electrically associated with a second AC power signal level,
determine an operating frequency from an operating frequency range for the driving signal, the operating frequency associated with a third AC power signal level that is greater than the first AC power signal level and less than the second AC power signal level,
generate the driving signal based on the operating frequency, and
provide the power control signal to the external power supply.
|