| CPC H01M 8/0693 (2013.01) [H01M 8/04186 (2013.01); H01M 8/0444 (2013.01); H01M 8/04753 (2013.01); H01M 8/188 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
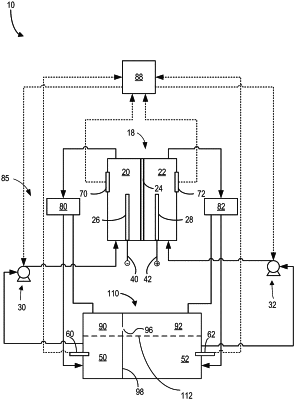
1. A redox flow battery system, comprising:
a cell receiving electrolyte and hydrogen gas;
a rebalancing reactor fluidly coupled to the cell and configured to also receive the electrolyte and the hydrogen gas; and
a conductive wire embedded in a catalyst bed of the rebalancing reactor, the conductive wire configured to apply a negative potential to the catalyst bed to impede formation of a double diffusion layer and increase a ferrous iron reduction rate at the catalyst bed.
|