| CPC H01L 29/872 (2013.01) [H01L 23/66 (2013.01); H03B 19/06 (2013.01); H01L 2223/6627 (2013.01); H01L 2223/6688 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
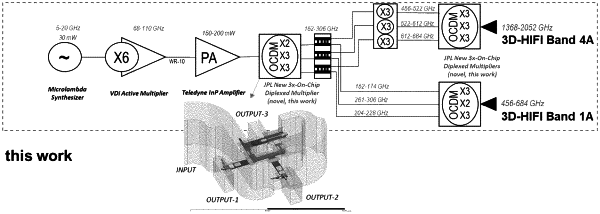
1. A multiplier or mixer solid-state device, comprising:
a chip comprising two or more on-chip diplexed frequency multiplying or mixer structures including diodes, transmission lines, chip to waveguide transitions, and a waveguide structure where the multiplying or mixer structures are placed, wherein:
the structures include on-chip diplexing distributing a broadband input signal, transmitted onto the chip, among the two or more of the multiplier or mixing structures with narrower RF operation bandwidth,
each of the multiplying or mixer structures comprises two or more diodes and is tuned to work in a certain frequency band, comprising a frequency sub-band of the broadband input signal's frequency band,
the diodes each comprise at least one anode, one ohmic contact and a semiconductor heterostructure,
the diodes on each of the structures are balanced in terms of electrical behavior,
the diodes each generate a higher frequency through frequency-multiplication of the input frequency in the frequency sub-band transmitted to the each of the diodes, or an intermediate frequency through frequency mixing of two input frequencies in the frequency sub-band transmitted to the each of the diodes,
each of the signals generated in the diodes of one of the multiplying or mixing structures are electrically combined to form an output signal comprising a combined output frequency band,
each of the output signals generated in each of the multiplying or mixing structures can be coupled to the same or different output waveguide(s) using output E-probes located on each of the structures radiating directly to the same or different output waveguide(s), and
each of the two or more multiplying structures work at a different one of the frequency sub-bands within the input signal's frequency band, so that the input signal is automatically divided into the two or more multiplying structures without the need of additional waveguide based diplexers.
|