| CPC G16C 20/30 (2019.02) | 16 Claims |
|
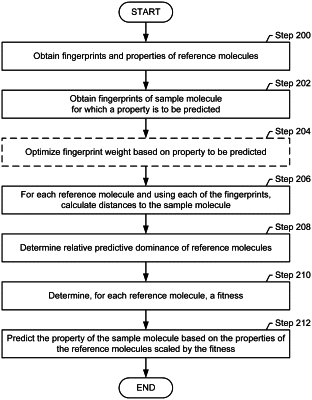
1. A computer-implemented method for predicting a property of a sample molecule, the computer-implemented method comprising:
for each of a plurality of reference molecules, obtaining a plurality of fingerprints and at least one property;
obtaining the plurality of fingerprints of the sample molecule;
for each of the plurality of reference molecules, using each of the plurality of fingerprints, calculating distances to the sample molecule in a multi-dimensional feature space wherein a dimensionality of the multi-dimensional feature space corresponds to a number of the plurality of fingerprints;
for each of the plurality of reference molecules, determining a relative predictive dominance, based on the distances to the sample molecule, wherein determining the relative predictive dominance comprises obtaining a scoring vector by comparing a first distance between a first reference molecule of the plurality of reference molecules and the sample molecule and a second distance between a second reference molecule of the plurality of reference molecules and the sample molecule within the multi-dimensional feature space;
for each of the plurality of reference molecules, determining an associated fitness value based on the relative predictive dominance wherein the associated fitness value quantifies a measure of similarity between each of the plurality of reference molecules relative to the sample molecule; and
predicting the at least one property of the sample molecule based on the at least one property of each of the plurality of reference molecules and the associated fitness value for each of the plurality of reference molecules by obtaining a majority vote on the at least one property by each of the plurality of reference molecules and scaling a contribution by each of the plurality of reference molecules to the majority vote by the associated fitness value.
|