| CPC G06V 10/774 (2022.01) [G06T 5/20 (2013.01); G06T 5/70 (2024.01); G06T 7/0002 (2013.01); G06T 11/001 (2013.01); G06V 10/273 (2022.01); G06V 10/759 (2022.01); G06V 10/776 (2022.01); G06V 10/82 (2022.01); G06T 2207/10056 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30024 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30168 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
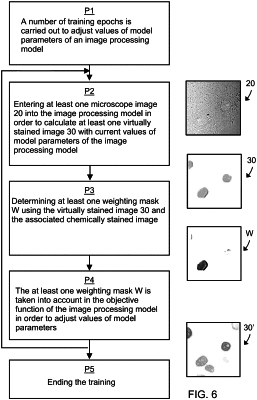
1. A computer-implemented method for generating an image processing model in order to calculate a virtually stained image from a microscope image, comprising:
training of the image processing model using training data, wherein the training data comprises at least:
microscope images as input data into the image processing model, and
target images that are formed via chemically stained images registered locally in relation to the microscope images;
wherein the image processing model is trained to calculate virtually stained images from the input microscope images by optimizing an objective function that captures a difference between the virtually stained images and the target images;
defining at least one weighting mask after a number of training steps using at least one of the chemically stained images and an associated virtually stained image calculated after the number of training steps;
wherein, in the weighting mask, one or more image regions are weighted based on differences between locally corresponding image regions in the virtually stained image and in the chemically stained image; and
continuing the training, wherein the weighting mask is taken into account in the objective function.
|