| CPC G06T 17/20 (2013.01) [A61C 1/082 (2013.01); B29C 64/393 (2017.08); B33Y 50/02 (2014.12); B29L 2031/7546 (2013.01); B33Y 80/00 (2014.12); G06T 2210/36 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
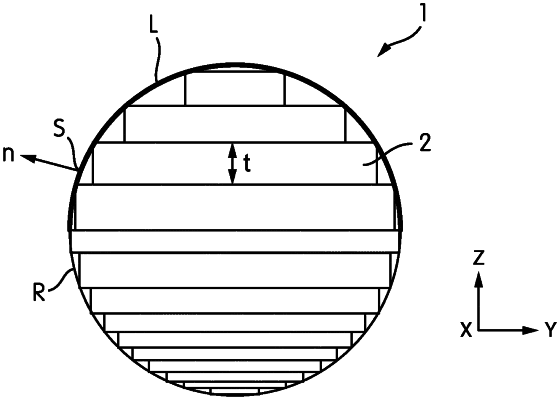
1. A method of determining layer thicknesses (t) of a three-dimensional model for generation of a corresponding three-dimensional object with an additive manufacturing apparatus, the method comprising:
determining the layer thicknesses (t) according to an adaptive slicing algorithm in which the thickness of a layer is calculated through a relation which defines a reference precision requirement (R), and is based on the inclination of the normal vectors (n) of the surface elements (s) of the 3D model which at least partly enclose the layer from a horizontal direction (x;y),
the method further comprising:
selectively imposing on at least one surface element (s) of the 3D model a precision requirement out of one or more selectable different precision requirements which respectively differently alter in the determination the relation with respect to the inclination of the normal vector (n) of the said at least one surface element (s),
wherein the one or more selectable different precision requirements comprise at least one of
a high precision requirement which allows, through the altered relation, the layer thickness (t) to obtain a value smaller than the layer thickness (t) determined through the unaltered relation; and
a low precision requirement (L) which allows, through the altered relation, the layer thickness (t) to obtain a value larger than the layer thickness (t) determined through the unaltered relation, and
wherein the reference precision requirement (R) is between the low precision requirement (L) and the high precision requirement and,
wherein among the layer thicknesses (t) calculated for surface elements (s) corresponding to the same layer through the said relation and imposed through the one or more differently altered relations, the smallest value is determined as the layer thickness (t).
|