| CPC G06F 17/11 (2013.01) [G06N 10/00 (2019.01); H10N 60/12 (2023.02)] | 16 Claims |
|
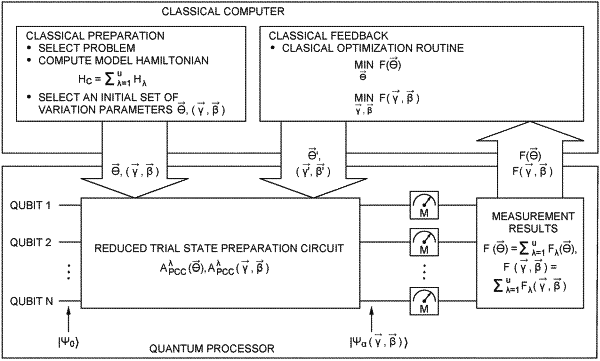
1. A method of performing computation in a hybrid quantum-classical computing system comprising a classical computer and a quantum processor, comprising:
computing, by the classical computer, a model Hamiltonian onto which a selected problem is mapped, wherein the model Hamiltonian comprises a plurality of sub-Hamiltonians;
executing iterations, each iteration comprising:
setting the quantum processor in an initial state, wherein the quantum processor comprises a plurality of Josephson junctions, each of which has two frequency-separated states defining a superconducting qubit;
transforming the quantum processor from the initial state to a trial state based on each of the plurality of sub-Hamiltonians and an initial set of variational parameters by applying a first trial state preparation circuit to the quantum processor;
measuring an expectation value of each of the plurality of sub-Hamiltonians on the quantum processor; and
selecting, by the classical computer, another set of variational parameters based on a classical optimization method, if a difference between the measured expectation values of the model Hamiltonian in a current iteration and a previous iteration is more than a predetermined value; and
outputting the measured expectation value of the model Hamiltonian as an optimized solution to the selected problem.
|