| CPC G01S 7/5209 (2013.01) [A61B 8/14 (2013.01); A61B 8/463 (2013.01); A61B 8/465 (2013.01); A61B 8/469 (2013.01); A61B 8/5238 (2013.01); G01S 15/8977 (2013.01); G06T 5/00 (2013.01); G06T 5/50 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10132 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20221 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. An ultrasound beamforming method, comprising:
obtaining channel data from echoes returned from a target tissue;
performing at least two beamforming processes on the channel data using at least two different ultrasound beamforming methods to obtain at least two image data frames of the target tissue corresponding to the at least two different ultrasound beamforming methods, wherein the at least two beamforming processes are performed on the same channel data, and each of the ultrasound beamforming methods correspondingly obtains one image data frame, and the at least two different ultrasound beamforming methods are different in at least one of a principle, a step, and a parameter; and
fusing the at least two image data frames of the target tissue to obtain a fused ultrasound image of the target tissue, wherein the fusing comprises:
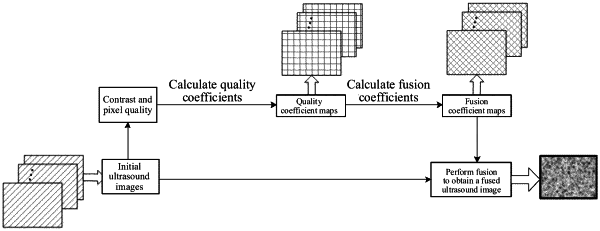
respectively generating, according to the at least two image data frames, at least two initial ultrasound images of the target tissue corresponding to the at least two different ultrasound beamforming methods;
for each pixel in each of the at least two initial ultrasound images, determining a fusion coefficient of each pixel according to a contrast and a pixel quality of each pixel, to obtain at least two fusion coefficient maps corresponding to the at least two initial ultrasound images, respectively, wherein the contrast of each pixel in each initial ultrasound image is positively correlated with a pixel value change amount of the pixel relative to a neighboring pixel, the pixel quality of each pixel in each initial ultrasound image is negatively correlated with a difference between a pixel value of the pixel and a pixel median value, and the fusion coefficient of each pixel is positively correlated with the contrast and the pixel quality; and
fusing the at least two initial ultrasound images of the target tissue according to the at least two fusion coefficient maps respectively corresponding to the at least two initial ultrasound images, to obtain the fused ultrasound image of the target tissue.
|