| CPC G01M 7/025 (2013.01) [G01C 25/005 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
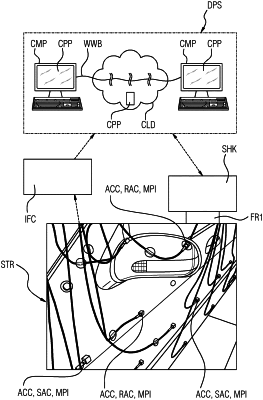
1. A System for analyzing the motions of a mechanical structure, the system comprising:
a plurality of standard accelerometers configured to measurement-points of the mechanical structure;
at least three reference accelerometers configured to measurement-points of the mechanical structure;
at least one shaker attached to the mechanical structure for moving the structure periodically within a first frequency range; and
at least one data processing system configured to:
receive measurements from the at least three reference accelerometers at the measurement-points when periodically moving the mechanical structure within the first frequency range by the at least one shaker and
calibrate the positions and orientations of the plurality of standard accelerometers by the following steps:
determining from the measurements of the at least three reference accelerometers rigid body motions,
determining positions and orientations of the plurality of standard accelerometers from the rigid body motions, wherein determining positions and orientations further comprises:
decomposing the 6 rigid body motions applying an infinitesimal rotation model into six infinitesimal rigid body translation-rotation pairs by solving a resulting set of linear equations using a solver,
linearly recombining said six infinitesimal rigid body translation-rotation pairs into three pure translations,
deriving orientations of the plurality of standard accelerometers from the three pure translations, and
deriving positions of the plurality of standard accelerometers from the 6 rigid body motions.
|