| CPC E02F 9/2841 (2013.01) [E02F 9/2825 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
1. A retaining mechanism for teeth, comprising:
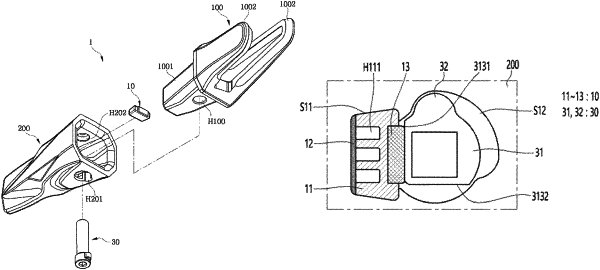
a tooth point having a coupling space that comprises a first space and a second space communicating with each other;
a damper structure accommodated in the first space, and comprising a flexible portion having an insertion groove which is positioned on one surface thereof and a hollow therein extending from the one surface to another surface opposite to the one surface and having one side which is open, a hard portion inserted in the insertion groove and having one surface which is a flat surface and is exposed to an outside, and a sealing portion blocking the opened side of the hollow; and
a coupling unit accommodated in the second space, a portion of which is in contact with the one surface of the hard portion in an initial state, in which the coupling unit is inserted into the second space,
wherein the sealing portion is an element separated from the tooth point,
wherein coupling of the flexible portion and the sealing portion is made in a fitting operation using a protrusion,
wherein, in response to rotation of the coupling unit in the second space from the initial state, another portion different from the portion of the coupling unit comes into contact with the hard portion,
wherein when the coupling unit rotates in one direction from the initial state to become a first rotation state a portion where the coupling unit and the hard portion contact each other is moved in a direction toward the flexible portion further than the initial state, and thus, the hard portion is moved in the direction toward the flexible portion further than the initial state, and
wherein the flexible portion is compressed and deformed between the hard portion and an inner surface of the tooth point forming the first space.
|