| CPC C23C 16/4417 (2013.01) [C04B 35/581 (2013.01); C04B 35/62685 (2013.01); C04B 35/62805 (2013.01); C04B 35/6281 (2013.01); C04B 35/62815 (2013.01); C04B 35/62884 (2013.01); C04B 35/62894 (2013.01); C23C 16/0227 (2013.01); C23C 16/0272 (2013.01); C23C 16/40 (2013.01); C23C 16/405 (2013.01); C23C 16/45536 (2013.01); C23C 16/45544 (2013.01); C23C 16/505 (2013.01); H01L 21/68757 (2013.01); C04B 2235/3225 (2013.01); C23C 16/442 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A deposition method, comprising:
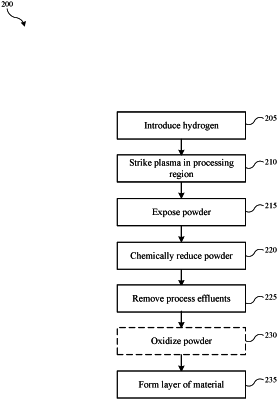
introducing hydrogen into a processing chamber, a powder disposed within a processing region of the processing chamber, and wherein the powder comprises a passivation layer;
striking a first plasma in the processing region, the first plasma comprising energetic hydrogen species;
exposing the powder to the energetic hydrogen species in the processing region;
chemically reducing the powder through a reaction of the powder with the energetic hydrogen species, wherein chemically reducing the powder removes the passivation layer;
removing process effluents including unreacted hydrogen from the processing region;
forming a first layer of material on grains of the powder within the processing region, wherein the first layer of material comprises yttrium oxide, cerium oxide, titanium oxide, calcium oxide, or magnesium oxide; and
forming a second layer of material overlying the first layer of material, wherein the second layer of material comprises a different material than the first layer of material, and wherein the second layer of material comprises yttrium oxide, cerium oxide, titanium oxide, calcium oxide, or magnesium oxide.
|