| CPC B22D 41/58 (2013.01) [B22D 11/117 (2013.01); B22D 41/42 (2013.01)] | 5 Claims |
|
1. A method for maintaining an optimal argon injection flow rate for a chosen alloy composition during casting to produce optimal steel cleanliness in a cast steel, the method comprising:
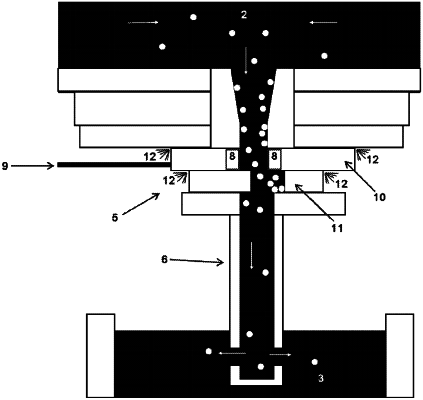
a) providing an argon injected slide gate controlling the flow of liquid steel through a nozzle;
b) selecting a steel having a steel composition to be cast, the selected steel having a known optimal argon injection flow rate Qb* for the selected steel;
c) determining a present injection flow rate conductance Gb′ of the argon injected slide gate using either
a formula: Gb′=(M/B)×Qa′, wherein Qa′ is an average argon flow rate during a steel pressure change event, M is a slope of a line on a graph having an x-axis and a y-axis, the graph plotting a steel pressure and an argon pressure during the steel pressure change event, the steel pressure plotted on the x-axis of the graph and the argon pressure plotted on the y-axis of the graph, and B is the y-intercept of the line, or
a formula: Gb′=B/(M*Ps), wherein Ps is a steel pressure immediately after an argon flow change event, B is a y-intercept of a line on a graph having an x-axis and a y-axis, the graph plotting an argon flow and an argon pressure during the argon flow change event, the argon flow plotted on the x-axis and the argon pressure plotted on the y-axis, and M is a slope of the line;
d) calculating a present steel pressure Ps′, wherein the present steel pressure is calculated by multiplying a present height of the steel above the argon injection point multiplied by the density of the steel composition times the acceleration due to gravity;
e) calculating a required present argon pressure Pa′ to provide the optimal argon injection flow rate Qb*, using the equation Pa′=Qb*/Gb′+Ps′;
f) adjusting a present argon pressure to the calculated required present argon pressure Pa′;
g) casting the selected steel with the steel composition while injecting argon into the selected steel at the optimal argon injection flow rate Qb*;
h) repeating at least one of the steps c) to g) a plurality of times until all of the selected steel has been cast.
|