| CPC B01D 17/04 (2013.01) [B01D 17/0205 (2013.01); B08B 9/0321 (2013.01); C10G 9/16 (2013.01); C10G 75/00 (2013.01); F28G 9/00 (2013.01); F28G 15/003 (2013.01); B08B 2209/032 (2013.01); C10G 2300/4075 (2013.01); C10G 2300/807 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
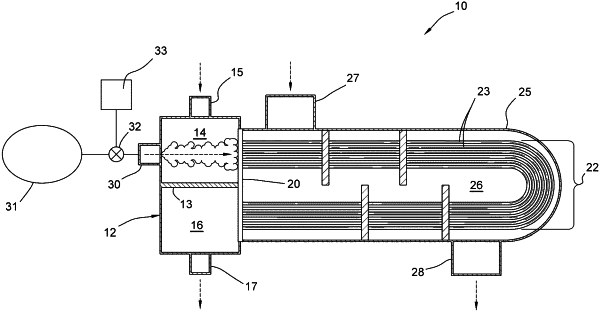
1. A process for operating an industrial device for heating a process fluid where the process fluid includes components that are prone to causing fouling or forming deposits on one or more surfaces within the industrial device, comprising:
a) directing the process fluid into the industrial device at a desired flow rate,
wherein the industrial device comprises a housing and a plurality of tubes that passes through the housing,
wherein the plurality of tubes comprises an inlet plenum that comprises a first inlet that receives the process fluid and a second inlet that receives a source of steam,
wherein an internal volume inside the plurality of tubes comprises a tube side chamber that conveys the process fluid from the inlet plenum through the tube side chamber,
wherein a space between an outside of the plurality of tubes and the housing defines a shell-side chamber,
wherein the shell side chamber and the tube side chamber are sealed from each other, and the shell side chamber receives a heating fluid;
b) heating the process fluid within the industrial device to produce a heated process fluid by conducting heat from the heating fluid in the shell side chamber to the process fluid in the tube side chamber as the process fluid stream moves along the one or more surfaces within the industrial device where foulants may form and deposit or adhere to the one or more surfaces;
c) periodically injecting steam into the inlet of plenum via the second inlet the industrial device at a rate in excess of the desired flow rate for the process fluid and in sufficient quantity to create a higher flow rate and an increase in turbulent two-phase flow of the steam and the process fluid within the tube side chamber to dislodge at least one of a foulant and a fouling precursor from one or more surfaces of the tube side chamber; and
d) directing the heated process fluid out of the tube side chamber, wherein the heated process fluid contains at least one of the foulant, fouling precursor, or both.
|