| CPC A61M 5/30 (2013.01) [A61M 5/2046 (2013.01); A61M 11/02 (2013.01); A61M 11/001 (2014.02); A61M 11/06 (2013.01)] | 5 Claims |
|
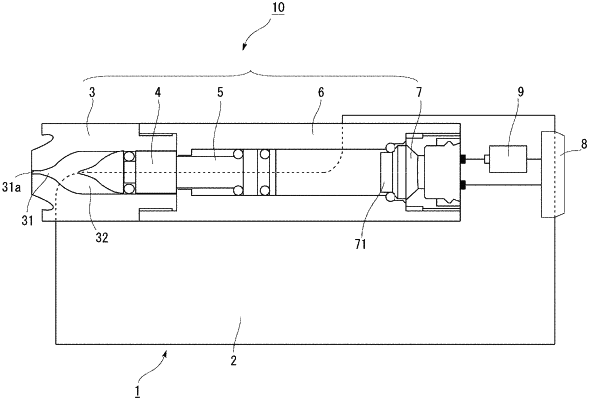
1. A needleless injector that injects a solution containing biomolecules into an injection target the injector comprising:
a filling chamber configured to accommodate a solution containing biomolecules;
a drive comprising a gas generating agent configured to generate a gas;
a nozzle including an injection port configured to inject the solution containing biomolecules into the injection target, wherein the injection target comprises biomolecules therein configured to function in the injection target; and
a piston configured to pressurize the solution containing biomolecules based on the generated gas, prior to the solution containing biomolecules being injected into the injection target, at an injection pressure rate of 6.8×104 MPa/s or more and at an injection pressure of being less than 25 MPa such that a proportion of the biomolecules functioning in the injection target with respect to the injected biomolecules is higher after the solution containing biomolecules is injected into the injection target than before the solution containing biomolecules is injected into the injection target,
wherein the injection pressure rate is defined as a change in an injection pressure of the solution containing biomolecules per unit time from an injection start time of the solution containing biomolecules to a time of 0.20 ms, and wherein the injection pressure is defined as an injection pressure of the solution containing biomolecules from the injection start time of the solution containing biomolecules to 4.0 ms.
|