| CPC A61B 5/1495 (2013.01) [A61B 5/14532 (2013.01); A61B 5/1468 (2013.01); A61B 5/14865 (2013.01); A61B 5/6849 (2013.01); A61B 5/686 (2013.01); G01N 27/026 (2013.01); G06N 5/022 (2013.01); G16H 20/17 (2018.01); G16H 40/40 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); G16H 50/70 (2018.01); A61B 5/0075 (2013.01); A61B 5/02055 (2013.01); A61B 5/021 (2013.01); A61B 5/024 (2013.01); A61B 5/1118 (2013.01); A61B 5/14546 (2013.01); A61B 5/1455 (2013.01); A61B 5/7203 (2013.01); A61B 5/7221 (2013.01); A61B 5/7267 (2013.01); A61B 5/742 (2013.01); A61B 2505/07 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0223 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0252 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0257 (2013.01); A61B 2562/028 (2013.01); A61B 2562/029 (2013.01); A61B 2562/164 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
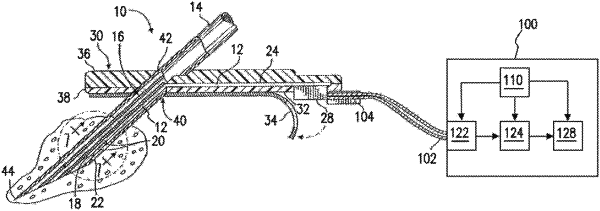
1. A method for external calibration of a glucose sensor used for measuring a level of glucose in a body of a user, the glucose sensor including physical sensor electronics, a microcontroller, and a working electrode, the method comprising:
accessing electrode current (Isig) signals for the working electrode, the Isig signals being measured by the physical sensor electronics;
accessing Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) related data for the working electrode, the EIS-related data generated by an EIS procedure;
based on the Isig signals and the EIS-related data and a plurality of calibration-free sensor glucose (SG)-predictive models, calculating, by the microcontroller, a respective SG value for each of the SG-predictive models;
fusing, by the microcontroller, the respective SG values for the SG-predictive models to calculate a single, fused SG value;
calculating, by the microcontroller, a modification factor based on a value of a physiological calibration factor (PCF), a value of an environmental calibration factor (ECF), or both;
determining, by the microcontroller, whether the calculated modification factor is valid; and
in a case where the modification factor is determined to be valid:
calculating, by the microcontroller, a single, calibrated, fused SG value based on the modification factor and the single, fused SG value;
performing, by the microcontroller, error detection diagnostics on the calibrated, fused SG value to determine whether a correctable error exists in the calibrated, fused SG value;
in a case where it is determined that the correctable error exists, correcting, by the microcontroller, the correctable error; and
displaying a corrected, calibrated, fused SG value to the user,
wherein the PCF is based on status information of an activity level, a heart rate, a blood pressure, and a body temperature of the user.
|