| CPC H04W 72/1263 (2013.01) [H04W 72/0446 (2013.01); H04W 72/23 (2023.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A method performed by an access node, the method comprising :
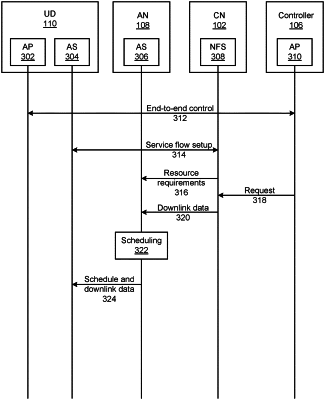
receiving, from a core network (CN) , dynamic resource requirements for uplink transmissions corresponding to downlink transmissions of data between the access node and a user device, wherein both the uplink transmissions and the downlink transmissions correspond to closed-loop control events;
receiving, from the CN, downlink data destined for the user device with an indication that real-time feedback from the user device is expected;
determining, based on the received dynamic resource requirements, an adaptive schedule for the received downlink data and for expected uplink data corresponding to the received downlink data, wherein:
the adaptive schedule comprises a downlink schedule for the received downlink data and an uplink schedule for the expected uplink data, and
the downlink schedule is included in a physical downlink control channel (PDCCH), the PDCCH further comprising an indication that the uplink schedule will be included in a message that also includes the received downlink data;
configuring the adaptive schedule to account for real-time network conditions and user device characteristics corresponding to closed-loop control events, wherein the closed-loop control events each include a downlink transmission followed by a synchronous uplink transmission, and parallel closed-loop control events occur isochronously for multiple user devices; and
sending the adaptive schedule to the user device, wherein the determination of the adaptive schedule, and the sending of the adaptive schedule, are performed by the access node for each user device individually.
|