| CPC H04Q 11/0062 (2013.01) | 7 Claims |
|
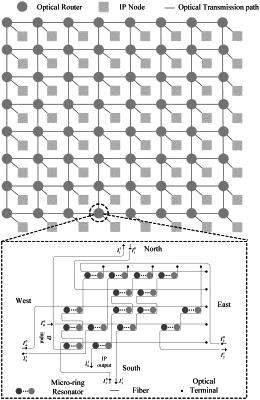
1. A low congestion routing method of an Optical Network-on-Chip (ONoC), wherein, the ONoC is an ONoC with a Mesh topology; an electrical router and an optical router connecting to a same IP router have same coordinates with the IP router; and the method comprises:
sending, by a source IP node, a route setup request to a first electrical router connected to the source IP node; wherein, the route setup request comprises coordinates of the source IP node and coordinates of a destination IP node; and coordinates of the first electrical router are the same as the coordinates of the source IP node;
receiving, by the first electrical router, the route setup request from the source IP node; determining a first target output port according to congestion information of buffer queues in transmittable directions and random numbers through an arbitration; sending the route setup request to the destination IP node through the first target output port;
receiving, by the destination IP node, the route setup request; analyzing information about the source IP node in the route setup request; generating an Acknowledge (ACK) packet; sending the ACK packet to a second electrical router connected with the destination IP node; wherein, the second electrical router is connected with the destination IP node and coordinates of the second electrical router are the same as the coordinates of the destination IP node;
receiving, by the second electrical router, the ACK packet from the destination IP node; determining a second target output port according to congestion information of buffer queues in transmittable directions and random numbers through an arbitration; sending the ACK packet to the source IP node through the second target output port; locking the second target output port; controlling an optical router having the same coordinates as the second electrical router to turn on a micro-ring resonator in a corresponding direction; wherein, the corresponding direction refers to a direction opposite to a transmission direction of the ACK packet;
receiving, by the source IP node, the ACK packet; transmitting the ACK packet to an optical transmission port;
performing, by the source IP node, an Electro-Optical (E/O) conversion on the ACK packet to obtain an optical information packet; sending the optical information packet to a first optical router connected to the source IP node;
receiving, by the first optical router, the optical information packet from the source IP node; sending the optical information packet through a micro-ring resonator in the corresponding direction to the second optical router connected to the destination IP node; controlling the first electrical router having the same coordinates as the first optical router to open the second target output port;
receiving, by the second optical router, the optical information packet; sending the optical information packet to the destination IP node; receiving, by the destination IP node, the optical information packet; and performing an Optical-Electro (O/E) conversion on the optical information packet; wherein,
the congestion information comprises: the number of packets buffered;
the determining a first target output port according to congestion information of buffer queues in transmittable directions and random numbers through an arbitration comprises:
determining a port of a first transmittable direction and a port of a second transmittable direction of the first electrical router according to the coordinates of the source IP node, the coordinates of the destination IP node and directions of ports of the first electrical router connecting with other electrical routers;
determining a first arbitration range for the port of the first transmittable direction based on the number of packets in a first buffer queue of the port of the first transmittable direction;
determining a second arbitration range for the port of the second transmittable direction based on the number of packets in a second buffer queue of the port of the second transmittable direction;
generating a first random number according to the first arbitration range;
generating a second random number according to the second arbitration range; and
determining the first target output port according to the first random number and the second random number; and
the determining a second target output port according to congestion information of buffer queues in transmittable directions and random numbers through an arbitration comprises:
determining a port of a third transmittable direction and a port of a fourth transmittable direction of the second electrical router according to the coordinates of the destination IP node, the coordinates of the source IP node and directions of ports of the second electrical router connecting with other electrical routers;
determining a third arbitration range for the port of the third transmittable direction based on the number of packets in a third buffer queue of the port of the third transmittable direction;
determining a fourth arbitration range for the port of the fourth transmittable direction based on the number of packets in a fourth buffer queue of the port of the fourth transmittable direction;
generating a third random number according to the third arbitration range;
generating a fourth random number according to the fourth arbitration range; and
determining the second target output port according to the third random number and the fourth random number.
|