| CPC H02J 50/30 (2016.02) [H02J 50/40 (2016.02); H02J 50/80 (2016.02); H04B 10/807 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
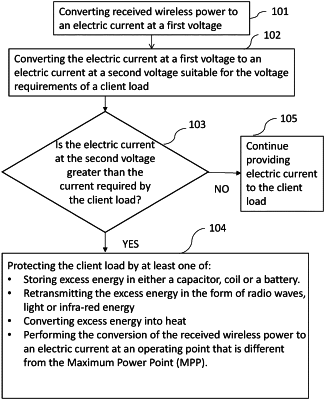
1. A method of controlling the electrical power output of a device wirelessly charged by a wireless power beam, the method comprising:
converting the received wireless power to an electric current at a first voltage;
converting the electric current at the first voltage to an electric current at a second voltage suitable for the voltage requirements of a client load; and
if the level of the wireless power input to the device increases, such that the electric current at the second voltage is greater than the current required by the client load, thereby endangering the client load, in addition to, or as an alternative to storing the excess energy generated by the current in excess of that required by the client load, either in a capacitor, a coil or a battery, performing at least one off:
(i) retransmitting the excess energy from the device in the form of radio waves, light or infra-red energy;
(ii) converting the excess energy into heat; or
(iii) performing the conversion of the received wireless power to an electric current at an operating point that is different from the Maximum Power Point (MPP).
|