| CPC G16H 20/10 (2018.01) [G16H 50/30 (2018.01); G16H 50/70 (2018.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method, comprising:
automatically switching, by an ingestible transmitter, from a deactivated state into a transmitting state responsive to exposure to stomach acid of a patient, the ingestible transmitter associated with a first medication ingested by the patient, the ingestible transmitter deactivated during manufacturing of the ingestible transmitter;
transmitting, by an ingestible transmitter to a computer system, an indicator responsive to ingestion of the first medication by the patient and exposure to the stomach acid;
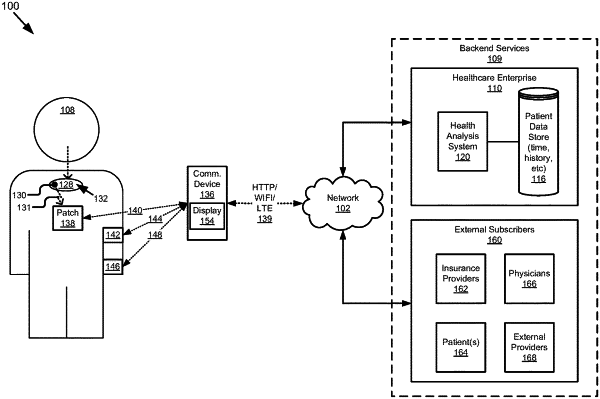
collecting, by a first sensor associated with the patient, the indicator, the indicator identifying a first adherence event at a first indicator time indicating at least the first medication was ingested by the patient;
receiving, by a computer system, the indicator, the indicator collected from the ingestible transmitter and by the first sensor associated with the patient, the indicator identifying the first adherence event at the first indicator time indicating at least the first medication was ingested by the patient, the first medication associated with the ingestible transmitter, and the ingestible transmitter automatically transmitting the indicator responsive to ingestion of the first medication by the patient;
collecting, by a second sensor associated with the patient, physiological data of the patient including first physiological data collected after the indicator and second physiological data collected prior to the indicator;
in response to detection of the indicator, receiving, by the computer system, the first physiological data of the patient collected, by the second sensor associated with the patient, after the indicator;
receiving, by the computer system, the second physiological data collected, by the second sensor associated with the patient, prior to the indicator;
determining, by the computer system, a history of medication ingested by the patient based on receipt of indicators associated with one or more adherence events, wherein the history of medication ingested by the patient indicates whether first medication was taken as prescribed or whether one or more doses were missed;
determining, by the computer system, a medication administration history of the physiological data of the patient based on the history of the medication ingested by the patient, the first physiological data, and the second physiological data; and
predicting, by the computer system and based on a comparison of the medication administration history of the physiological data of the patient to peer group data, a medical condition of the patient and an out-of-range efficacy, wherein:
the peer group data includes one or more medication administration histories associated with one or more peer patients comprising a peer group;
one or more of the peer group data and the medication administration history of the physiological data of the patient include at least one missed dose, thereby including at least one instance where the first medication was not taken as prescribed; and
the out-of-range efficacy is a degree to which the first medication effects a physiological response of the patient, when taken as prescribed, that is outside of a normal range.
|