| CPC G16B 20/20 (2019.02) [G16B 20/10 (2019.02); G16B 40/20 (2019.02); G16H 10/40 (2018.01); G16H 50/70 (2018.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented machine learning method for identifying cancer-cell specific transcriptional output for provision of immunotherapy treatment, the method comprising:
receiving, by a processor, the nucleic acid data from one or more samples;
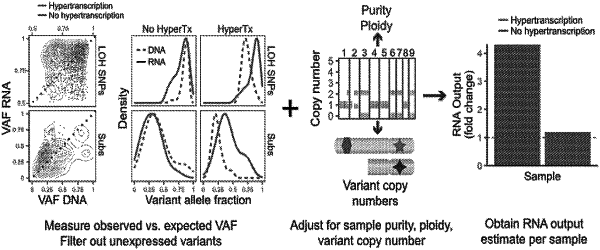
determining, by the processor, variant allele fraction (VAF) of markers in ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleic acid data and markers for deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in the nucleic acid data;
comparing, by the processor, the VAF of the RNA relative to the DNA for each of the markers;
quantifying, by the processor, cancer-cell specific changes in transcriptional output for each of the markers using the comparison of the VAF of the RNA relative to the DNA;
inputting input data comprising the quantification of cancer-cell specific changes to a machine learning regression model, the machine learning regression model having been trained on input data comprising ratios of RNA relative to DNA to determine that a higher ratio of RNA relative to the DNA indicates a higher mutation burden and more aggressive cancer, the machine learning regression model generating as output data a mutation burden;
identifying, by the processor, a response to immunotherapy treatment using the mutation burden where low mutation burden indicates non-hypermutant tumors that respond to the immunotherapy treatment; and
outputting, by the processor, the response to immunotherapy treatment for provision of the immunotherapy treatment of cancer.
|