| CPC G10L 25/78 (2013.01) [G10L 25/18 (2013.01); G10L 25/30 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
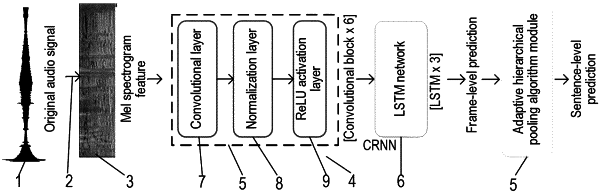
1. A weakly-supervised sound event detection method based on adaptive hierarchical pooling, comprising:
extracting an acoustic feature of a pre-processed audio signal, inputting the acoustic feature to an acoustic model, dividing a frame-level prediction probability sequence predicted by the acoustic model into a plurality of consecutive sub-bags, calculating significant information of each of the sub-bags through maximum pooling to obtain a sub-bag-level prediction set, and obtaining an average probability of the sub-bag-level prediction set through mean pooling as a sentence-level prediction probability;
jointly optimizing the acoustic model and a relaxation parameter until convergence to obtain an optimal model weight and an optimal relaxation parameter, and formulating an optimal pooling strategy for each category of sound event based on the optimal relaxation parameter; and
performing pre-processing and feature extraction on a given unknown audio signal to obtain a pre-processed audio signal, inputting the pre-processed audio signal to a trained acoustic model to obtain frame-level prediction probabilities of all target sound events to complete an audio locating task, and obtaining sentence-level prediction probabilities of all categories of the target sound events based on the optimal pooling strategy of each category of the target sound events to complete an audio classification task.
|