| CPC G06N 10/00 (2019.01) [H03K 19/173 (2013.01)] | 26 Claims |
|
14. An apparatus comprising:
a classical processor;
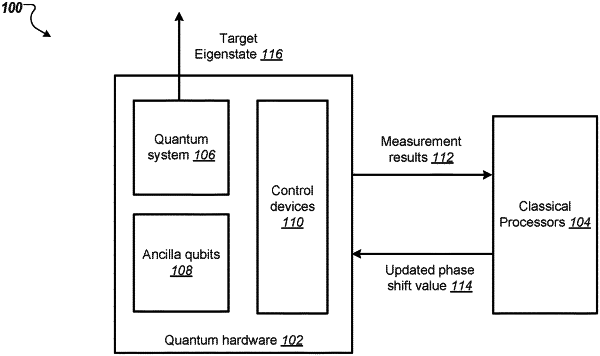
a quantum computing device comprising:
a quantum system prepared in an initial state, wherein the initial state has non-zero overlap with a target eigenstate;
one or more ancilla qubits each prepared in a zero computational basis state;
a plurality of control lines coupled to the quantum system and the one or more ancilla qubits; and
a plurality of control circuits coupled to the plurality of control lines, the plurality of control circuits configured to iteratively apply a quantum eigenstate locking circuit to the quantum system and one or more ancilla qubits until the state of the quantum system approximates the target eigenstate, wherein iteratively applying the quantum eigenstate locking circuit to the quantum system and one or more ancilla qubits comprises, at each batch of n iterations:
for each iteration in the batch:
preparing the ancilla qubit in the zero computational basis state;
applying a first Hadamard gate to the ancilla qubit;
applying a phase gate to the ancilla qubit, the phase gate applying a phase shift between the zero computational basis state and a one computational basis state of the ancilla qubit, wherein the phase shift is the same for each iteration in the batch;
applying a controlled operation to the quantum system and ancilla qubit, the controlled operation controlling evolution of the quantum system under the Hamiltonian for a time t, wherein the ancilla qubit acts as a control;
applying a second Hadamard gate to the ancilla qubit; and
measuring the ancilla qubit to determine an ancilla qubit state;
wherein at each batch of iterations the classical processor is configured to:
determine an estimated current average energy of the quantum system based on (i) an average of the ancilla qubit state for the batch, (ii) the time t used in the batch, and (iii) the phase shift applied by the phase gate for the batch; and
updated the phase shift applied by the phase gate to the ancilla qubit for the next batch of iterations such that the updated phase shift is equal to the estimated current average energy of the quantum system multiplied by the time t.
|