| CPC G06F 30/23 (2020.01) [E04G 23/08 (2013.01); G06F 2119/14 (2020.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
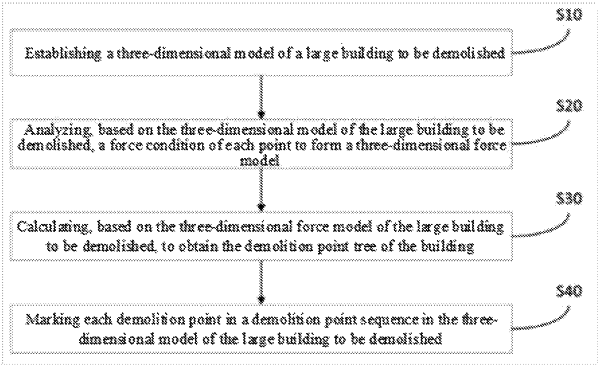
1. A method for determining demolition points of a large building, comprising the following steps:
S10, establishing a three-dimensional model of a large building to be demolished;
S20, analyzing, based on the three-dimensional model of the large building to be demolished, a force condition of each point to form a three-dimensional force model;
S30, calculating, based on the three-dimensional force model of the large building to be demolished, to obtain a demolition point tree of the building; wherein the demolition point tree comprises a plurality of demolition points, a root node of the demolition point tree is a plurality of independent demolition points, and the demolition points are gridded to branch demolition points and leaf demolition points; and
S40, marking each demolition point in a demolition point sequence in the three-dimensional model of the large building to be demolished;
wherein the step of analyzing, based on the three-dimensional model of the large building to be demolished, a force condition of each point to form a three-dimensional force model specifically comprises:
establishing a global coordinate system in the three-dimensional model of the large building to be demolished;
gridding the three-dimensional model of the large building to be demolished to a plurality of grid units, wherein points in each of the grid units have similar mechanical characteristics;
calculating, based on the material density of the building and the volume of the grid unit, the mass of each grid unit;
calculating, for each grid unit, the gravity action to which it is subjected;
calculating, for each grid unit, the supporting force to which it is subjected;
adding the gravity action and the supporting force action of each grid unit to obtain the total force to which it is subjected;
mapping the total force of each grid unit to the three-dimensional model of the building to form the three-dimensional force model;
wherein the step of gridding the three-dimensional model of the large building to be demolished to a plurality of grid units specifically comprises:
step 1: extracting geometric information from the three-dimensional model of the large building to be demolished;
step 2: gridding the building based on the structural characteristics and geometric information of the building;
step 3: calculating force data of points in each grid unit, which is a combination of the gravity and support force;
step 4: calculating a mean force value of all points in each grid unit as a reference value;
step 5: calculating a difference between the force values and the reference values of all points, if the ratio of the absolute value of the difference to the reference value is greater than 33%, determining that the grid unit corresponding to the point does not meet the force requirements, and re-gridding that grid unit; and
step 6: repeating step 5 until no points that do not meet the force requirements exist;
wherein the step of calculating, based on the three-dimensional force model of the large building to be demolished, to obtain the demolition point tree of the building specifically comprises:
establishing a force matrix based on the three-dimensional force model of the large building to be demolished;
calculating a force balance condition based on the force matrix;
identifying, based on the force balance condition, a unit with the minimum force as a candidate demolition point; and
constructing the demolition point tree based on the relationship between candidate demolition points.
|