| CPC G06F 30/20 (2020.01) | 11 Claims |
|
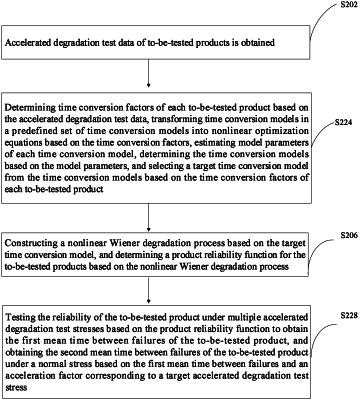
1. A method for processing accelerated degradation test data based on Wiener process, comprising:
constructing a nonlinear Wiener degradation process based on a target-time conversion model, and determining a product reliability function for the to-be-tested products based on the nonlinear Wiener degradation process; and
testing reliabilities of the to-be-tested products based on the product reliability function, and obtaining product reliability test results of the to-be-tested products to provide information of the to-be-tested product lifespan;
wherein the product reliability test results include a mean time between failures to indicate the to-be-tested products' quality over time and ability to maintain functionality within a specified time period;
wherein the product reliability test result further comprises a first mean time between failures and a second mean time between failures; and
wherein the testing the reliabilities of the to-be-tested products based on the product reliability function, and obtaining the product reliability test results of the to-be-tested products comprises:
testing the reliability of each to-be-tested product under multiple accelerated degradation test stresses based on the product reliability function, and obtaining the first mean time between failures of the to-be-tested product; and obtaining the second mean time between failures of the to-be-tested product under a normal stress based on the first mean time between failures and an acceleration factor corresponding to a target accelerated degradation test stress.
|