| CPC G01N 33/48721 (2013.01) [G01N 27/44791 (2013.01); G01N 33/5438 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
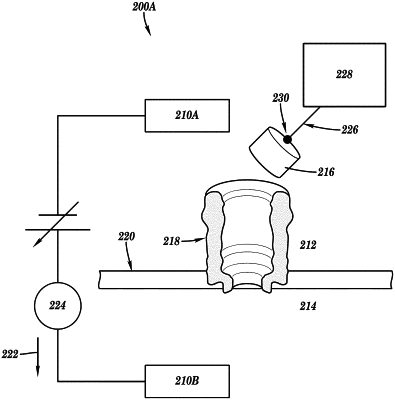
1. A Cytolysin A (ClyA) nanopore sensor comprising:
a support structure separating a first fluidic chamber from a second fluidic chamber;
at least one ClyA nanopore disposed in the support structure with an inlet of the at least one ClyA nanopore fluidically connected to the first fluidic chamber and an outlet of the at least one nanopore fluidically connected to the second fluidic chamber; and
a protein shuttle which comprises an electrically charged protein molecule comprising avidin, wherein the electrically charged protein molecule has a radial extent that is at least as large as a smallest diameter of a lumen of the at least one ClyA nanopore;
wherein the protein shuttle further comprises at least one linking species, wherein the linking species is attached to the electrically charged protein molecule and is configured to link the protein shuttle to at least one target molecule;
and wherein the electrically charged protein molecule is configured to be electrically driven into the ClyA nanopore.
|