| CPC G01H 9/004 (2013.01) [G01D 5/35361 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
1. A vehicle-assisted, buried cable localization method using distributed fiber optic sensing (DFOS), the method comprising:
providing a length of optical fiber having a portion thereof buried underground;
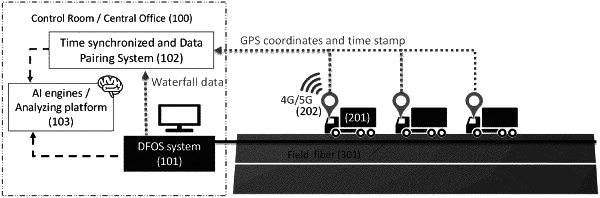
providing a DFOS system, said system including
a DFOS interrogator and analyzer in optical communication with the length of optical fiber, said DFOS interrogator configured to generate optical pulses from laser light, introduce the pulses into the length of optical fiber and detect/receive Rayleigh reflected signals from the optical fiber, said analyzer configured to analyze the Rayleigh reflected signals and generate location/time waterfall plots from the analyzed Rayleigh reflected signals;
operating a set of at least three vehicles in coordination with one another, said vehicles being operated sufficiently proximate to at least a portion of the length of optical fiber to provide mechanical excitations to the portion of the length of optical fiber, wherein each vehicle of the set of at least three vehicles includes a global positioning system (GPS) that generates GPS coordinates for the vehicle in which it is included;
operating the DFOS system while the set of at least three vehicles are being operated, thereby providing mechanical excitations to the portion of the optical fiber thereby producing vibration events in the optical fiber and recording DFOS signals received during DFOS operation;
continuously operating the DFOS system and the vehicles and determining time/location of vibration events from waterfall plots a associating the vibration events to a GPS location of the buried portion of the optical fiber.
|