| CPC G01B 11/2513 (2013.01) [G01B 11/254 (2013.01); G01B 11/2522 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
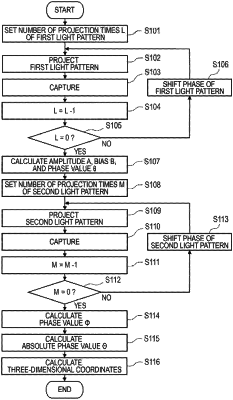
1. A three-dimensional shape measuring method comprising:
projecting, by a projector, a first light pattern having a luminance that changes at a first cycle on a measured object;
acquiring at least three first images of the measured object on which the first light pattern has been projected at different phases of the first phases;
projecting, by the projector that projected the first light pattern, a second light pattern having a luminance that changes at a second cycle that is different from the first cycle on the measured object;
acquiring a single second image of the measured object on which the second light pattern has been projected;
for each of the at least three first images, calculating, based on first luminance values of the first image at each of a plurality of positions on the object, relative phase values on the positions of the measured object;
calculating, based on the relative phase values and the first luminance values, a parameter of a relational expression representing a relationship between luminance and phase;
calculating, based on second luminance values of the single second image, based on the relative phase values calculated at the positions on the measured object, and based on the parameter, absolute phase values for the positions of the measured object, wherein only one image of the measured object on which the second light pattern has been projected is used in calculating the absolute phase values, the only one image being the single second image; and
calculating, based on the absolute phase values, three-dimensional coordinates at each of the positions on the measured object.
|