| CPC C12N 15/1131 (2013.01) [A61K 31/712 (2013.01); A61K 31/7125 (2013.01); A61K 47/549 (2017.08); A61P 31/20 (2018.01); C07H 21/02 (2013.01); C12N 15/111 (2013.01); C12N 2310/11 (2013.01); C12N 2310/314 (2013.01); C12N 2310/3145 (2013.01); C12N 2310/315 (2013.01); C12N 2310/3231 (2013.01); C12N 2310/341 (2013.01); C12N 2310/344 (2013.01); C12N 2310/351 (2013.01); C12N 2320/32 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. A chimeric antisense oligonucleotide represented by Formula (A):
5′-X-Y-Z3′ (A),
wherein
X-Y-Z is a chimeric oligonucleotide comprising a sequence of 18 to 22 nucleosides, optionally conjugated at the 5′ and/or 3′ end to a ligand targeting group;
X is a domain comprising a sequence of modified nucleosides that is 3 to 10 nucleosides in length;
Z is a domain comprising a sequence of modified nucleosides that is 3 to 10 nucleosides in length; and
Y is a domain comprising a sequence of 2 to 10 2′-deoxy-nucleosides linked through thiophosphate intersubunit linkages,
each modified nucleoside in the X domain and each modified nucleoside in the Z domain are nucleosides of Formula (1)
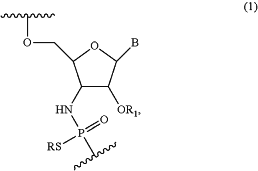 wherein
R is H or a positively charged counter ion,
B is a nucleobase independently selected from the group consisting of adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine, uracil, 5-methylcytosine, 2,6-diaminopurine, and 5-methyluracil,
R1 is —CR′3, —CR′2OCR′3, —(CR′2)3OCR′3, —(CR′2)1-2CR′3, —(CR′2)2OCR′3, or —Et, and
R′ is independently in each instance H or F, and
wherein the oligonucleotide comprises a nucleobase sequence that is complementary or hybridizes to a target RNA.
|