| CPC C03B 32/02 (2013.01) | 13 Claims |
|
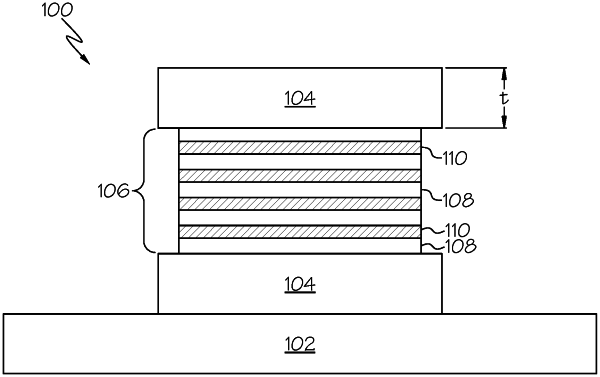
1. A method of ceramming a plurality of glass sheets comprising:
positioning the plurality of glass sheets in a stack between a first setter plate and a second setter plate in a glass stack configuration; and
exposing the glass stack configuration to a ceramming cycle to ceram the plurality of glass sheets into glass ceramic sheets,
wherein the first setter plate and the second setter plate each have:
a specific heat capacity of from about 670 J/kg*K to about 850 J/kg*K, as measured in accordance with ASTM E1461 at room temperature;
a bulk density of greater than about 2500 kg/m3, as measured in accordance with ASTM C20; and/or
a thermal diffusivity of greater than about 2.50×10−5 m2/s, and
further wherein at least one of the first setter plate be second setter plate has a porosity of less than about 1% and/or comprises at least 85 wt % reaction bonded silicon carbide.
|