| CPC B60L 53/122 (2019.02) [B60L 53/60 (2019.02); H02J 7/0047 (2013.01); H02J 50/12 (2016.02); H02J 50/80 (2016.02); H02M 5/293 (2013.01); B60L 2210/20 (2013.01); B60L 2210/30 (2013.01); H02J 2310/48 (2020.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
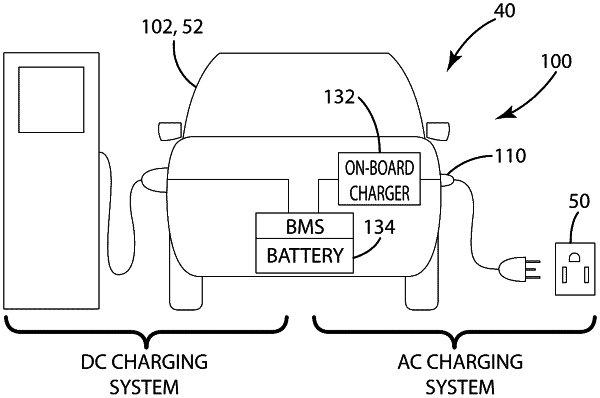
1. A system for wirelessly providing AC power to a vehicle or an energy storage system, the vehicle being an electric vehicle, a plug-in electric or a hybrid electric vehicle, the energy storage including a stationary or mobile energy storage element, the vehicle and the energy storage system including a battery, the system comprising:
an off-board module including:
an AC-to-AC bidirectional converter configured to receive a grid-voltage signal that is single phase, the AC-to-AC bidirectional converter configured to convert the grid-voltage signal to a modulated high-frequency voltage signal, wherein the modulated high-frequency voltage signal includes a high-frequency carrier signal having an envelope corresponding to the grid-voltage signal that is single phase or three-phase, wherein the AC-to-AC bidirectional converter includes two half bridges connected to single-phase active phases in a common point and configured such that, (i) during a positive cycle, a first one of the half bridges switches on-and-off the grid-voltage signal, while a second one of the half bridges does not switch, and (ii) during a negative cycle, the second one of the half bridges switches on-and-off the grid-voltage signal, while the first one of the half bridges does not switch, whereby the two half bridges chop the grid-voltage signal at a carrier frequency of the high-frequency carrier signal and produce the modulated high-frequency voltage signal, and
a transmitter including a primary coil, the transmitter configured to wirelessly transmit the modulated high-frequency voltage signal to the vehicle or energy storage battery;
an on-board module including:
a receiver including a pick-up coil, the receiver configured to
receive the modulated high-frequency voltage signal when the primary coil and the pick-up coil are disposed adjacent to each other, and
provide the modulated high-frequency voltage signal as AC power; and
an on-board AC charger configured to receive the AC power from the receiver, the AC power from the receiver being the modulated high-frequency voltage signal, the on-board AC charger configured to convert the AC power to DC power, and charge the battery with the DC power.
|