| CPC B23K 26/032 (2013.01) [B23K 26/0643 (2013.01); B23K 26/0648 (2013.01); B23K 26/082 (2015.10); B23K 26/16 (2013.01); G02B 19/0009 (2013.01); G02B 19/0047 (2013.01); G02B 26/101 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
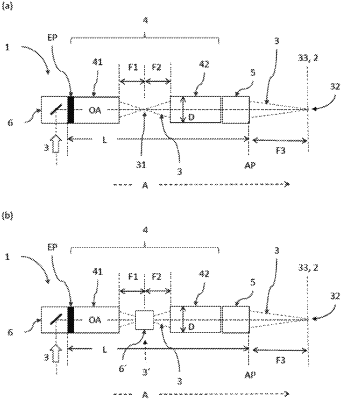
1. A device for processing hard-to-access workpieces by means of an imaging optical path, comprising a relay optical system with an optical axis passing through the relay optical system and with at least one first relay optical group, each having a plurality of first optical elements for generating a first focal length, and at least one second relay optical group, each having a plurality of second optical elements for generating second focal length, and a focusing unit arranged in the optical axis in a propagation direction of the imaging optical path with a plurality of optical elements for generating a third focal length which is formed after the second focal length, wherein a beam scanner arranged before the first relay optical group seen in the propagation direction of the imaging optical path, which beam scanner is provided both as an entrance pupil for the imaging optical path entering the first relay optical group and for at least controllably deflecting the imaging optical path in relation to the optical axis, the first relay optical group being adapted to focus the imaging optical path in an intermediate focus located separately from the first and the second relay optical group between the first and the second relay optical group, and the second relay optical group being adapted for imaging the intermediate focus for exit from the relay optical system and the focusing unit being adapted for focusing the imaging optical system in a focus of the device on a focus plane for processing of the workpiece,
whereby a distance between the entrance pupil and an end of the device in the direction of the imaging optical path is larger than the diameter of the largest optical element of the relay optical system, an optical shifting element being arranged in the imaging optical path before the beam scanner in the propagation direction of the imaging optical path, which shifting element allows continuous variation of the focus plane.
|