| CPC A61N 5/1049 (2013.01) [A61N 5/1075 (2013.01); G06F 17/18 (2013.01); A61N 2005/1057 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
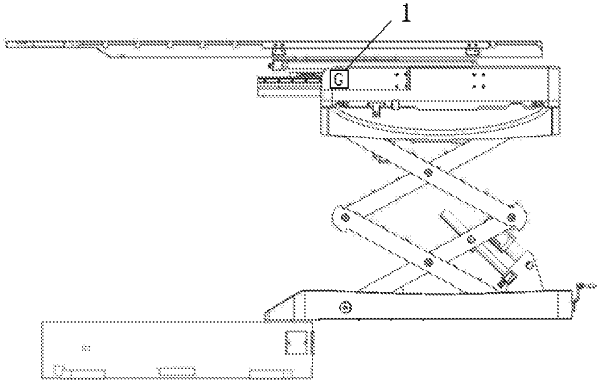
|
1. A compensation method for bed surface drop before and after accelerator radiotherapy bed comprising the following steps:
S1: within the range of the patient's weight G, decompose G into N weights on average, that is G=(G1, G2, . . . , Gi, . . . , GN), within the range of the couch top position L of moving the tumor to the isocenter position, decompose L into M positions on average, that is L=(L1, L2, . . . , Lj, . . . , LM);
S2: carry out an experiment, under the condition of constant weight Gi and length Lj, measure the drop amount Hij of the couch top through the experimental method to form a matrix HN×M, as shown below:
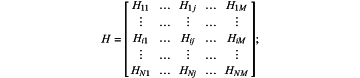 S3: in the case of a certain weight Gi, with H(Gi,L1), H(Gi,L2), . . . , H(Gi,Lj), . . . , H(Gi,LM) as the calculation node, the cubic spline curve S(Gi,L) of L is calculated by the cubic spline calculation method, and the average subdivision between Lj-1 and Lj is M1 parts, that is, Lj-1, Lj-1,1, . . . , Lj-1,M1-1, Lj, and through the cubic polynomial S(Gi, L), calculate
S(Gi,Lj-1),S(Gi,Lj-1,1), . . . ,S(Gj,Lj-1,M1-1),S(Gi,Lj);
S4: in the case of a certain length of Lj-1, Lj-1,1, . . . , Lj-1,M1-1, Lj, with H(G1, Lj-1,k), H(G2,Lj-1,k), . . . , H(Gi,Lj-1,k), . . . , H(GN,Lj-1,k) as the calculation node, the cubic spline curve S(G,Lj-1,k) of L is calculated by the cubic spline calculation method, and the average subdivision between Gi+1 and Gi is N1 parts, that is, Gi+1, Gi+1,1, . . . , Gi+1,N1-1, Gi, and through cubic polynomial S(G,Lj-1,k), calculate S(Gi+1,Lj-1,k), S(Gi+1,1,Lj-1,k), S(Gi+1,2,Lj-1,k), . . . , S(Gi+1,N-1,Lj-1,k), S(Gi,Lj-1,k);
S5: for the experimental measurement value matrix HN×M, by performing cubic spline interpolation on the rows, and then performing cubic spline interpolation on the columns, the resulting cubic spline interpolation matrix SN×N1, M×M1 of HN×M has N*N1 rows and M*M1 columns;
S6: the patient is lying on the treatment couch, and the actual weight G of the patient and the actual L of moving the tumor to the isocenter position are obtained, and the pixel point closest to the value is found, and the corresponding drop amount H is calculated by using this pixel point.
|