| CPC A61B 1/00006 (2013.01) [A61B 1/00009 (2013.01); A61B 1/043 (2013.01); A61B 1/045 (2013.01); A61B 1/05 (2013.01); A61B 1/0638 (2013.01); A61B 1/0655 (2022.02); A61B 1/0661 (2013.01); G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10016 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10024 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10068 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
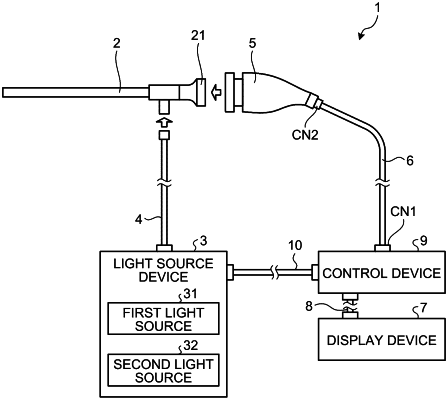
1. A medical observation system, comprising:
a light source configured to emit normal light of a first wavelength band and excitation light of a second wavelength band different from the first wavelength band;
an imaging device including an image sensor; and
circuitry configured to:
control the light source to emit alternately the normal light in a first period, and the excitation light in a second period following the first period,
control the imaging device to cause the image sensor to alternately perform capturing the normal light emitted from the light source and received by way of an observation target in the first period to generate a first captured image, and capturing the excitation light emitted from the light source and received by way of the observation target and fluorescence light from the observation target excited by the excitation light in the second period to generate a second captured image, wherein the normal light includes wavelengths of the fluorescence light,
perform an adjustment process to reduce a component of a color corresponding to the excitation light included in the second captured image,
perform a color changing process in which a color of a component of the fluorescence light having a luminance at a pixel position in the second captured image that exceeds a threshold included in the second captured image is changed into a specific color different from the color of the component of the fluorescence light, and
generate a superimposed image based on the first captured image and the second captured image subjected to the adjustment process,
wherein the adjustment process is a process in which each light component of colors corresponding to red, green, and blue wavelength bands included in the second captured image is multiplied by specific color correction information to reduce the component other than the component of the fluorescence.
|