| CPC G06N 5/04 (2013.01) [G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G16H 10/60 (2018.01); G16H 15/00 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01)] | 8 Claims |
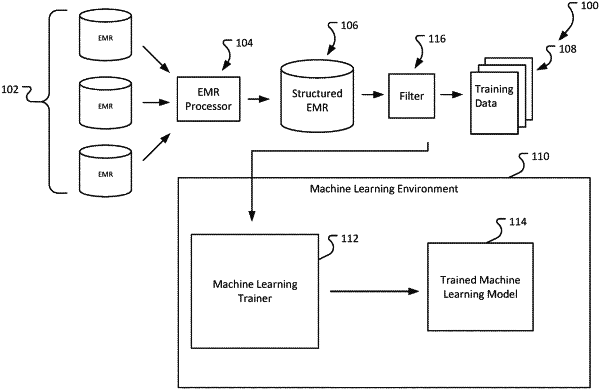
|
1. A method implemented by a computer system, the method comprising:
receiving data representing medical records of a patient, the patient having been diagnosed with diabetes mellitus;
generating a model input using the data representing the medical records of the patient;
determining a first predicted rate of hypoglycemic events by processing the model input using a first machine learning model that has been trained using first training data that comprises data representing medical records of a first plurality of patients and corresponding rates of hypoglycemic events for the respective patients, wherein each of the first plurality of patients uses a first type of insulin;
determining a second predicted rate of hypoglycemic events by processing the model input using a second machine learning model that has been trained using second training data that comprises data representing medical records of a second plurality of patients and corresponding rates of hypoglycemic events for the respective patients, wherein each of the second plurality of patients uses a second type of insulin, the second type of insulin being different from the first type of insulin, and the second plurality of patients being different from the first plurality of patients;
comparing the first predicted rate to the second predicted rate; and
recommending an insulin treatment for the patient based on the comparing.
|