| CPC G06F 16/21 (2019.01) [G06F 1/30 (2013.01); G06F 16/2455 (2019.01); G06F 16/252 (2019.01); G06F 16/972 (2019.01); H04L 67/1004 (2013.01); H04L 67/14 (2013.01); H04L 67/141 (2013.01); H04L 67/142 (2013.01); H04L 67/145 (2013.01); H04L 67/5681 (2022.05)] | 14 Claims |
|
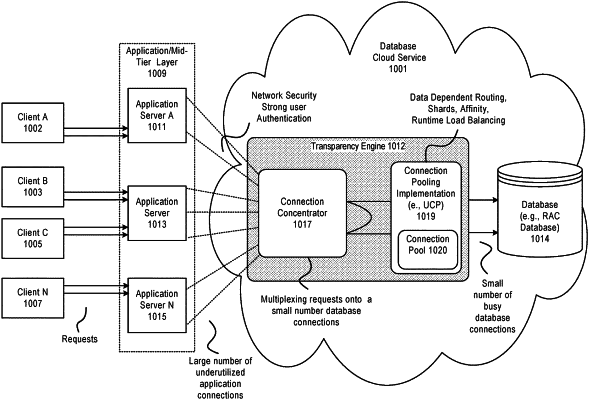
1. A system for connection concentration, comprising:
a microprocessor, and a software component executing thereon that provides connectivity between client applications and a database environment, including:
providing, for access by the client applications, a plurality of inbound connections that are shareable by the client applications and enable the client applications to communicate requests, via the inbound connections, to the database environment;
providing a plurality of outbound connections that operate to communicate received requests to the database environment;
multiplexing the inbound connections and the outbound connections for use with transaction requests, including maintaining one or more cursor maps for use with the inbound connections associated with the client applications and the outbound connections associated with the database environment;
associating one or more of the inbound connections with an application context associated with a client application and including an application connection identifier; and
selectively mapping the one or more inbound connections associated with the application context with one or more of the outbound connections, based on the application context for the client application and a session state, to provide a mapping of connections associated with the application context;
wherein the software component operates to provide a session abstraction layer for use by the client applications, including that a first client application can use a first driver type to connect to the database environment, and a second client application can use a second driver type to connect to the database environment;
wherein the software component tracks session states, request boundaries, and cursors to reuse database connections across the first and second client applications;
wherein the software component uses the application context, session states, request boundaries, and cursors, to match an application connection to a database connection in a connection pool, wherein in response to a request received from the client application, a request boundary is determined, and a connection pair provided within the mapping of connections associated with the application context is used to process the request, including one of retrieving a requested data from a cache or querying the database environment for the requested data.
|