| CPC G06F 1/28 (2013.01) [G06F 9/44505 (2013.01); G06F 1/30 (2013.01); G06F 1/3203 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. An integrated circuit (IC), comprising:
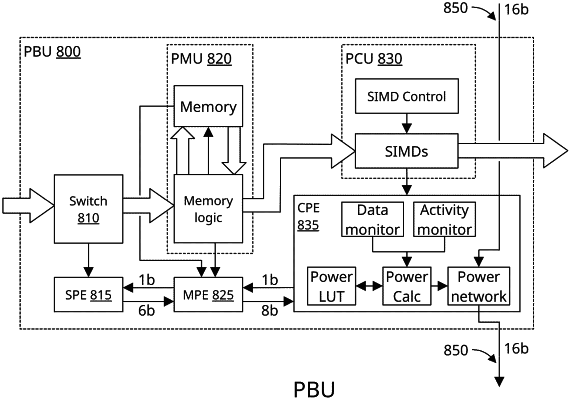
multiple power base units (multiple PBUs) arranged in an array of rows and columns, wherein a PBU includes a switch, a memory unit, a compute unit, a switch power estimator (SPE), a memory power estimator (MPE), and a compute power estimator (CPE);
dedicated wiring coupling the multiple PBUs with an array-level power accumulator; and
a power clock management controller (PCMC) coupled with the array-level power accumulator;
wherein:
the SPE is configured to estimate a nominal dynamic power dissipated in the switch;
the MPE is configured to estimate a nominal dynamic power dissipated in the memory unit;
the CPE is configured to estimate a nominal dynamic power dissipated in the compute unit;
the array-level power accumulator is configured to calculate an array-level nominal dynamic power estimate; and
the PCMC is configured to scale the array-level nominal dynamic power estimate with a frequency scale factor and/or a voltage scale factor, and to add a static power estimate to obtain a total power estimate.
|